Diagnosis and Treatment for Dysthymia
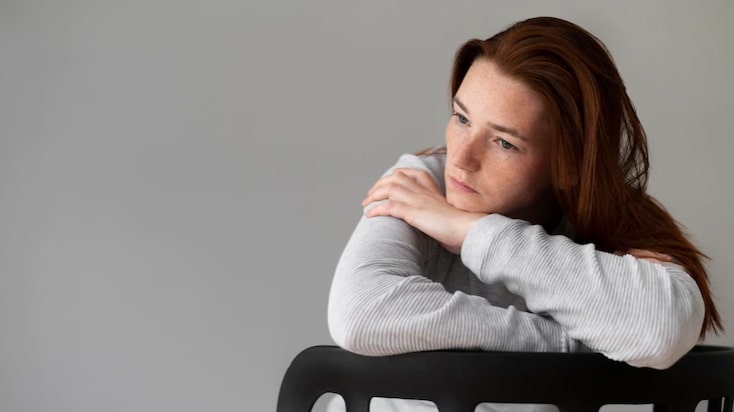

Dysthymia, also known as persistent depressive disorder, is a less severe but long-lasting form of depression. If you have this condition, you may also have periods of major depression. Experts do not know the cause of dysthymia, but genes may play a role. Major life stressors, chronic conditions, certain medications, and relationship or work problems can increase your chances of dysthymia if you are biologically predisposed to developing depression. Symptoms of dysthymia Bethesda are similar to those of major depression but are fewer and less intense. The symptoms may include sadness most of the day, a major change in weight or appetite, insomnia or excessive sleep, fatigue, suicidal thoughts, and concentration problems.
Diagnosis for dysthymia
During dysthymia diagnosis, your doctor will first perform a physical examination. The doctor may order blood tests and other laboratory screenings to rule out possible medical issues that may be causing your symptoms. For diagnosis in adults, you must have symptoms of dysthymia almost every day for two years or more. Children and teens must have a depressed mood or irritability most of the day, almost daily dot at least one year.
Treatment for dysthymia
Medications
Your doctor can recommend various types of antidepressants to treat dysthymia. They include:
Selective serotonin inhibitors like fluoxetine and sertraline.
Tricyclic antidepressants like amitriptyline and amoxapine.
Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors like desvenlafaxine and duloxetine.
Your doctor may suggest you try different medications and dosages to help you find an effective solution to your problem. Dysthymia treatment requires patience as most drugs take several weeks to have full effect. Do not stop taking medications as prescribed by your provider. Stopping treatment or missing doses can cause withdrawal-like symptoms or worsen your depressive symptoms.
Therapy
Combining medication and psychotherapy is the most effective way of treating dysthymia. Your therapist may suggest you go through psychotherapy or cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). Psychotherapy, also called talk therapy, involves sessions with your mental therapist. It can happen in group sessions, privately with your therapist, or remotely through phone or video.
CBT emphasizes your actions, behaviors, thoughts, and emotions. Your mental therapist will help you identify and deal with the factors causing your depression. The therapist helps you accept your symptoms and develop safe coping habits for your dysthymia. CBT can be a short-term therapy and help reduce the risk of future relapses.
Talking to a mental therapist can help you learn how to express your thoughts and feelings healthily, cope with your emotions and adjust to a life crisis. It can help you identify thoughts, behaviors, and emotions that trigger your dysthymia symptoms, replace negative beliefs with positive ones and set realistic goals for yourself.
Lifestyle changes
Dysthymia is a long-term disorder, so it is essential to participate actively in your treatment plan. Making certain lifestyle changes can complement medical therapies and help reduce symptoms. Lifestyle changes that can help manage dysthymia include exercising regularly, avoiding drugs and alcohol, and eating natural foods like fruits and vegetables.
Dysthymia is a less severe but long-lasting form of stress and depression. Your doctor can effectively treat and manage your dysthymia through medications, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. at Contact Washington Center for Women’s and Children’s Wellness (WCWCW) to schedule an appointment for dysthymia treatment to help overcome those suicidal thoughts.